Antibiotics Increase Risk of Juvenile Arthritis
By Editorial Staff
We generally think of
arthritis as a disease of aging, although in reality, it can strike anyone, regardless of age, race, gender or occupation. In fact, a recent study not only points out that our youth can be affected by the disease, but also that an all-too-common culprit may be to blame: antibiotic use.
In the study, childhood antibiotic exposure increased the risk of idiopathic (of unknown cause) juvenile arthritis in dose-dependent fashion compared to no exposure. In other words, the more doses of antibiotics received during childhood, the higher the risk of developing arthritis compared to receiving no doses.
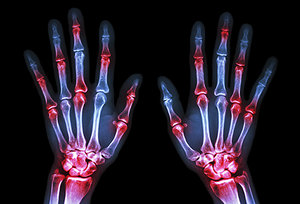 Specifically, any antibiotic use increased the risk by 110 percent, while five or more courses of antibiotics increased the risk by a whopping 200 percent compared to no use. The association between antibiotic use was strongest for exposures within one year of diagnosis.
Specifically, any antibiotic use increased the risk by 110 percent, while five or more courses of antibiotics increased the risk by a whopping 200 percent compared to no use. The association between antibiotic use was strongest for exposures within one year of diagnosis.
Unfortunately, this isn't the only negative health consequence associated with antibiotic use – just the latest reported in the peer-reviewed research literature. Talk to your doctor for more information, particularly before you fill that next antibiotic prescription. There may be a better (and definitely safer) way.

